Get full access with a free account
Benefits of the Coloplast® Professional Educational platform
- Full access to educational content, events and resources
- Track your progress
- Share content with your colleagues
- Share supporting material with your patient
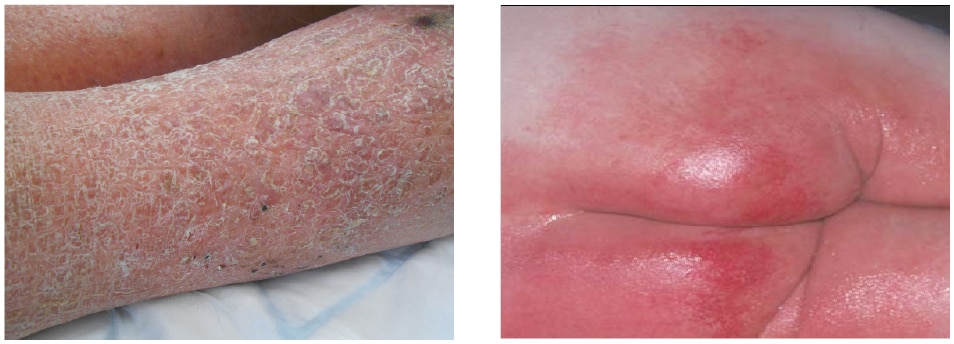
Damage to the Epidermis
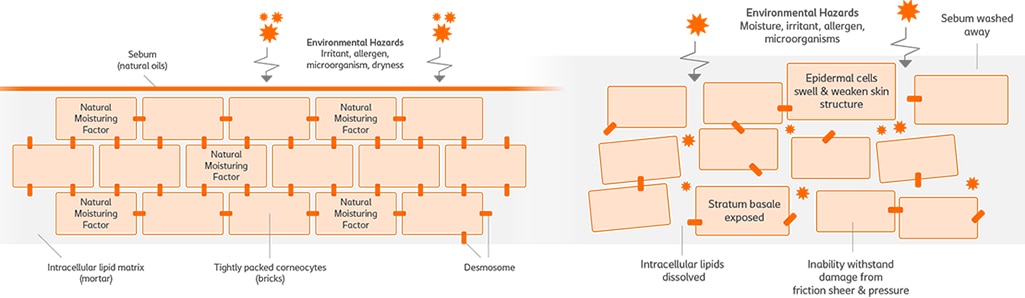
The epidermis plays an important role in keeping out harmful substances. However, if the skin becomes dehydrated, the cells in the epidermis shrink. This causes the epidermis to crack, which breaks down the skin barrier. Harmful substances can then enter the body through those cracks. The skin can lose its ability to retain moisture, and the epidermal barrier can be damaged.18
(See image below)
Age
 Aging affects all three skin layers in the following ways:
Aging affects all three skin layers in the following ways:
- The epidermis barrier function declines, making the skin more vulnerable.18
- As we get older, the amount of collagen and elastin fibres in our skin reduces. This makes the dermis thinner, which decreases skin elasticity and increases the risk of skin tears.2,18
- The subcutis also gets thinner as we age. This means we have less protection against mechanical injuries. Our cells don’t reproduce as quickly, and the rate of sebum secretion decreases as well. All of this leads to delayed healing and an increased risk of infection.18,27
pH levels
As we discussed in the previous section, the skin’s acid mantle helps to maintain the right pH balance on the skin. This, in turn, keeps bacteria levels low.18,33 The skin’s acidic pH, humidity and natural cleansing processes all help to maintain the skin’s barrier function and integrity.18 If the skin loses its acidity, this can make the skin vulnerable to damage and infection.18
Moisture
Maintaining the right moisture balance in the skin is important part of preserving the skin’s integrity. If the skin is too moist or too dry, it can damage the epidermis. For example, dry skin often itches. Scratching dry skin can damage the skin’s protective barrier. Dry skin also negatively affects the skin’s pH balance (see Factor #3 above). The combination of these factors increases the risk of skin infection.29
At the other extreme, exposing the skin to too much moisture for an extended period of time can cause ‘moisture-associated skin damage’ (MASD). MASD decreases the skin’s ability to protect the body.
This is one of the reasons why it’s is important to manage the level of moisture in a wound. To learn more about how to do that, visit the exudate management section.